Anatomy of the Nose
The normal anatomy of the nose is shown in Figures 1-3: the assorted terms used for nasal structures and dimensions (Fig. 1), the gristly parts of the nose and terms for regions (Fig. 2), and in Figure three the cross section is shown.
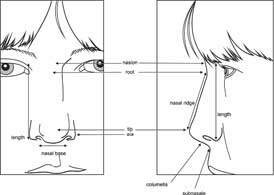
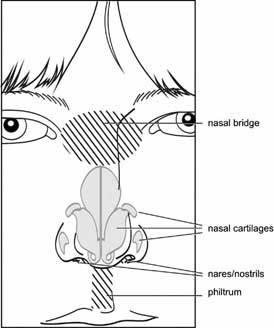
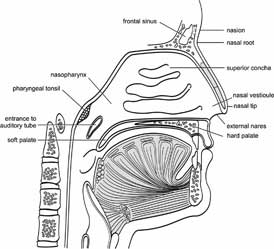
Some anatomical landmarks be specific mention as these don't seem to be perpetually used with normal that means.
Nasal Root:
The most depressed, superior a part of the nose on the nasal ridge.
Nasion:
The plane purpose simply superior to the nasal root superjacent the naso-frontal suture.
Nasal Bridge:
A saddle-shaped space that features the nasal root and also the lateral aspects of the nose. It lies between thecraniometric point and also the inferior boundary of the os nasale, and extends laterally to the inner canthi.
Nasal Ridge:
The plane prominence of the nose, extending from the nasal root to the tip (also referred to as the dorsum of the nose).
Nasal Base:
An notional line between the foremost lateral points of the external inferior attachments of the alae nasi to the face.
Nasal Tip:
The junction of the inferior margin of the nasal ridge and also the pillar. Commonly, it's the a part of the nose furthest from the plane of the face. In rare circumstances, like markedly outstanding and umbellate nasal profiles,different elements of the ridge is also additional far from the facial plane.
Ala:
The tissue comprising the lateral boundary of the nose, inferiorly, close the porta.
Columella:
The tissue that links the nasal tip to the nasal base, and separates the nares. it's the inferior margin of the septum.
Nasal Root:
The most depressed, superior a part of the nose on the nasal ridge.
Nasion:
The plane purpose simply superior to the nasal root superjacent the naso-frontal suture.
Nasal Bridge:
A saddle-shaped space that features the nasal root and also the lateral aspects of the nose. It lies between thecraniometric point and also the inferior boundary of the os nasale, and extends laterally to the inner canthi.
Nasal Ridge:
The plane prominence of the nose, extending from the nasal root to the tip (also referred to as the dorsum of the nose).
Nasal Base:
An notional line between the foremost lateral points of the external inferior attachments of the alae nasi to the face.
Nasal Tip:
The junction of the inferior margin of the nasal ridge and also the pillar. Commonly, it's the a part of the nose furthest from the plane of the face. In rare circumstances, like markedly outstanding and umbellate nasal profiles,different elements of the ridge is also additional far from the facial plane.
Ala:
The tissue comprising the lateral boundary of the nose, inferiorly, close the porta.
Columella:
The tissue that links the nasal tip to the nasal base, and separates the nares. it's the inferior margin of the septum.
Measurements of the Nose
Measurements of the nose area unit doable victimization slippery calipers. The reliableness of measurement semploying a tape is poor. moreover, the particular position of many of the landmarks could preclude correct activity. as an example, if the nasal tip overhangs the higher lip, the position of subnasale is tough to outline [Hall et al., [2007]]. Nasal length and dimension area unit the foremost common measurements taken in apply. a brief description of a way to live every dimension is provided because the numerous terms area unit outlined.
Growth of the nose doesn't finish at puberty: the nose continues to extend in size with age. There are not any traditional standards for nasal size in adulthood.
The reader is said the book of facts of traditional Physical Measurements [Hall et al., [2007]] for elaborate descriptions of activity techniques, further nasal measurements not delineated here, and growth standards. Most area unit accessible for Caucasians of Northern European extraction solely, and similar standards for alternative ethnicities area unit desperately required.
Growth of the nose doesn't finish at puberty: the nose continues to extend in size with age. There are not any traditional standards for nasal size in adulthood.
The reader is said the book of facts of traditional Physical Measurements [Hall et al., [2007]] for elaborate descriptions of activity techniques, further nasal measurements not delineated here, and growth standards. Most area unit accessible for Caucasians of Northern European extraction solely, and similar standards for alternative ethnicities area unit desperately required.
Anatomical Variation
Anomalies of the nose is also classified into quantitative traits and qualitative features:
Variations in length: long; short
Variations in width: wide nose; slender nose, broad nasal base; slender nasal base; broad nasal tip; slender nasal tip; wide nasal ridge; slender nasal ridge; wide nasal bridge; slender nasal bridge; broad pillar.
Variations long and width: distinguished nose; absent nasal cartilage; absent nose.
Variations in form or position: depressed nasal bridge; depressed nasal ridge; depressed nasal tip; bulbous nose;divided nasal tip; divided nose; overhanging nasal tip; deviated nasal tip; fullness of cavum tissue; distinguishednasal bridge; convexo-convex nasal ridge; planoconcave nasal ridge; low insertion of the columella; low hanging columella; short columella; high insertion of the columella; thick ala nasi; underdeveloped ala nasi; cleft ala nasi; enlarged naris; slender naris; single naris; proboscis; supernumerary naris; anteverted nares.
Variations in length: long; short
Variations in width: wide nose; slender nose, broad nasal base; slender nasal base; broad nasal tip; slender nasal tip; wide nasal ridge; slender nasal ridge; wide nasal bridge; slender nasal bridge; broad pillar.
Variations long and width: distinguished nose; absent nasal cartilage; absent nose.
Variations in form or position: depressed nasal bridge; depressed nasal ridge; depressed nasal tip; bulbous nose;divided nasal tip; divided nose; overhanging nasal tip; deviated nasal tip; fullness of cavum tissue; distinguishednasal bridge; convexo-convex nasal ridge; planoconcave nasal ridge; low insertion of the columella; low hanging columella; short columella; high insertion of the columella; thick ala nasi; underdeveloped ala nasi; cleft ala nasi; enlarged naris; slender naris; single naris; proboscis; supernumerary naris; anteverted nares.
No comments:
Post a Comment